
Physical Conditions
Why a Level I Trauma Center Matters
Where would you want to be in an emergency? In this article: The region's only Level I Trauma Center is at Carilion Roanoke Memorial Hospital (C...
 Eric Marvin, MDCranial and Skull Base Neurosurgery
Eric Marvin, MDCranial and Skull Base Neurosurgery"Developing relationships with my patients and seeing them satisfied with their surgical outcomes is absolutely the reason why I got into neurosurgery. "
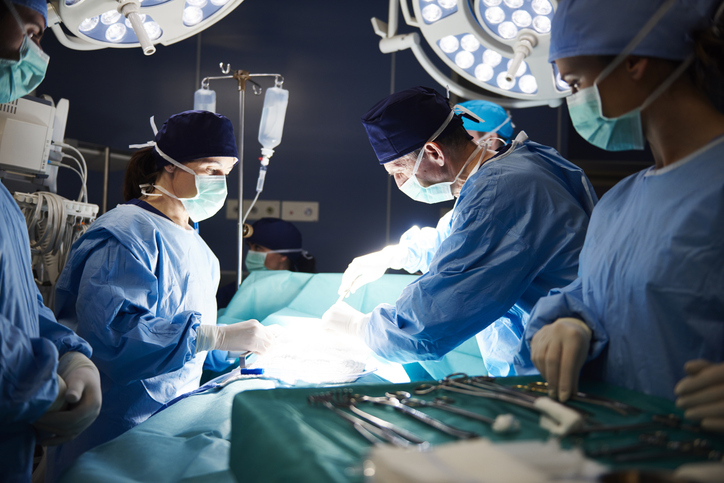
A craniotomy is the surgical removal of part of the bone from the skull to expose the brain. Specialized tools are used to remove the section of bone called the bone flap. The purpose of the procedure is to remove a brain tumor or a sample of brain tissue. It may also be done to remove blood or blood clots from the brain, relieve pressure in the brain after an injury or stroke, repair a skull fracture or brain aneurysm (a bulge in a blood vessel wall), or treat other brain conditions. The bone flap is replaced after the brain surgery has been done.
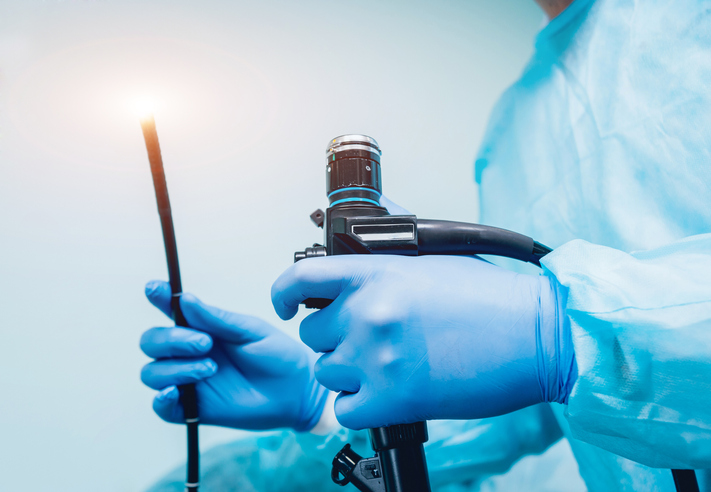
Endoscopic surgery is minimally-invasive, meaning it does usually not require a large incision. Neurosurgeons may make a small opening inside the nose to remove a growth through a thin lighted tube called an endoscope. An MRI is a type of picture taken of the skull base using magnets and a computer and may be done by a radiology specialist while the surgical specialists are operating to help them make sure all of the growth has been removed.
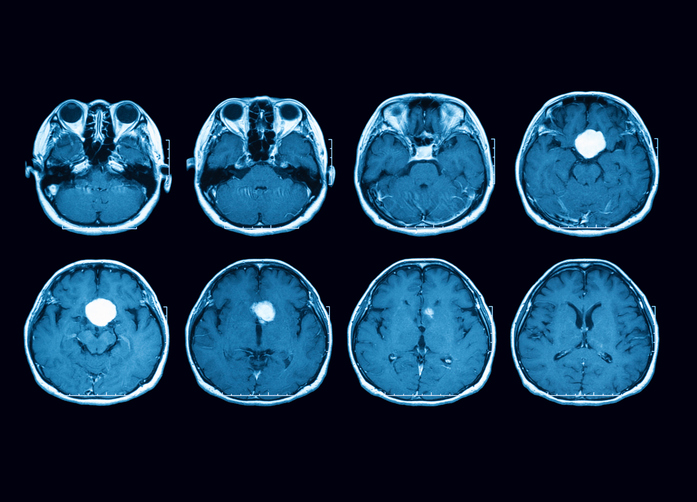
This is the most common way to remove pituitary tumors. Transsphenoidal surgery is done through the sphenoid sinus, a hollow space in the skull behind the nasal passages and below the brain. The back wall of the sinus is just below the pituitary gland.
This minimally invasive surgical tool removes hematomas with low tissue disruption, protecting parts of your brain that control speech, memory and vision. The neurosurgeon is able to navigate between the natural folds in the brain and map the exact location of the tumor or blood clot using imaging. Then, through an opening no larger than a dime, the neurosurgeon can remove the clot or tumor from the deepest recesses of the brain without cutting or damaging anything else in its path.
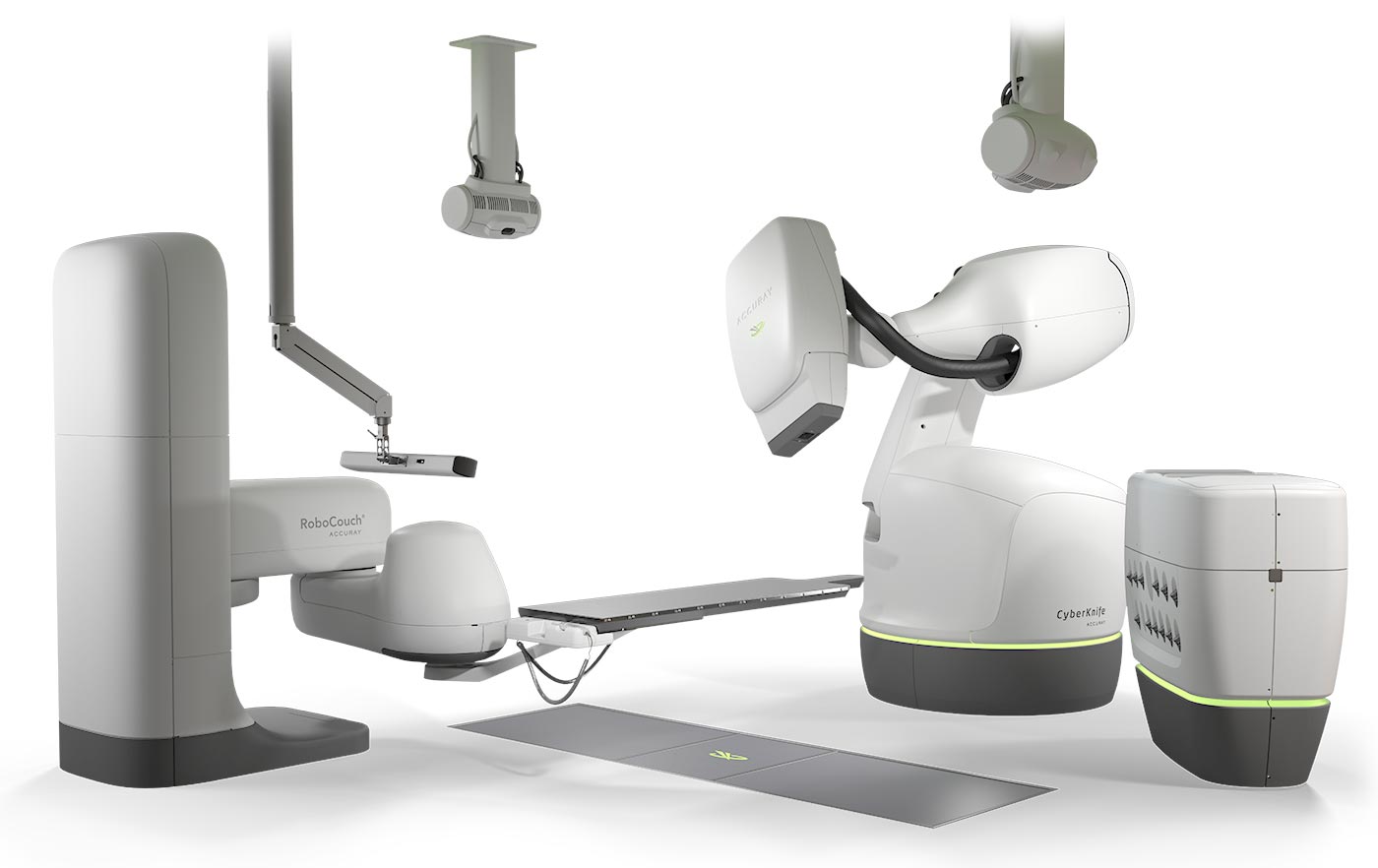
CyberKnife uses stereotactic body radiation therapy, delivering precise doses of radiation with extreme accuracy—accounting for tumor or patient movement in real-time. The robot moves and bends around the patient to deliver radiation doses from thousands of unique beam angles, significantly expanding the possible positions to concentrate radiation to the tumor while minimizing dose to surrounding healthy tissue.

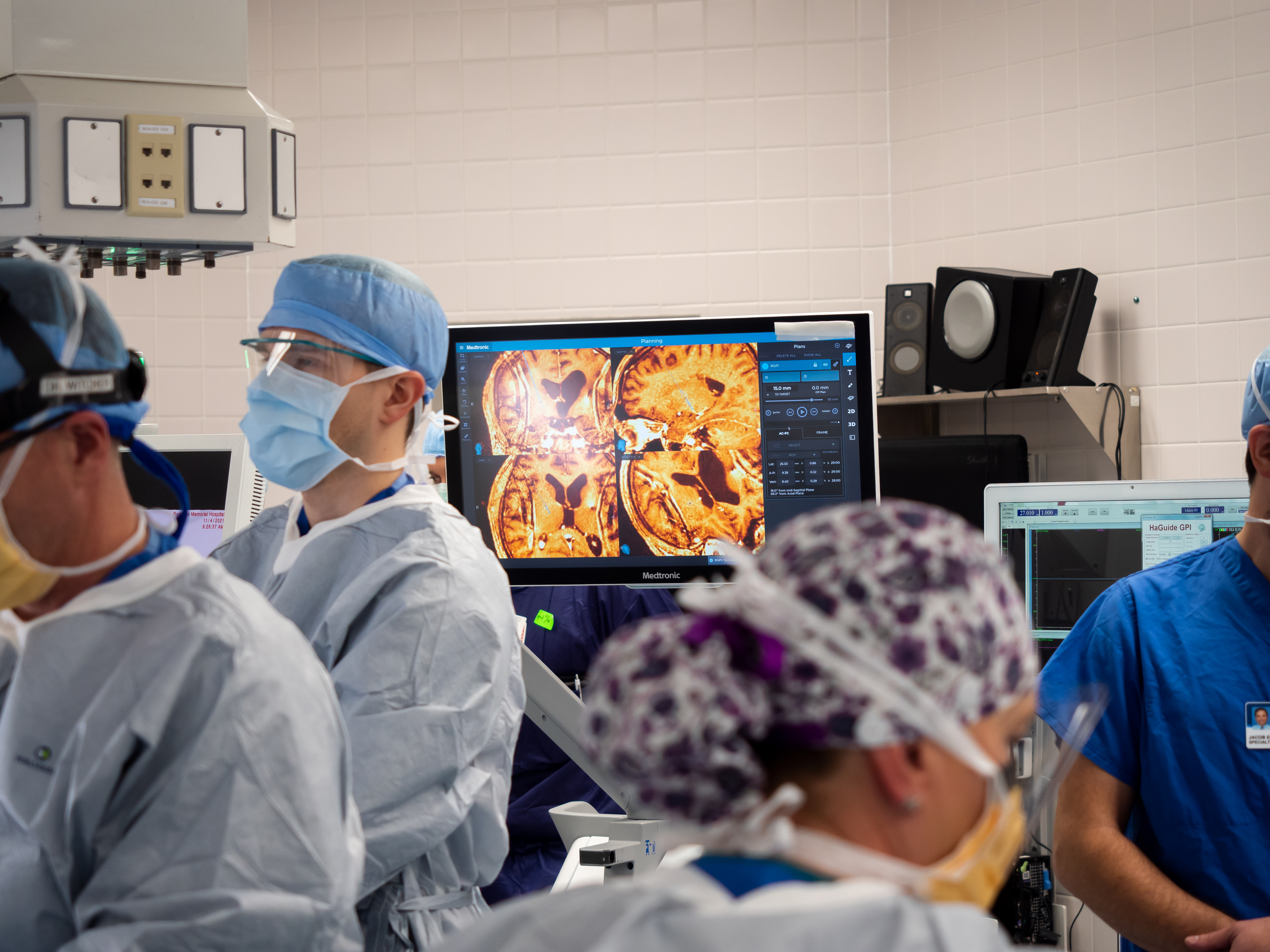
Neurosurgeons work closely with interventional radiologists, neurologists, oncologists and staff. Specialists contribute expertise in brain anatomy, skull base pathology, imaging, neurological function and oncological considerations. A collaborative effort ensures comprehensive patient evaluation, precise surgical planning, and optimal postoperative care, leading to improved outcomes.

A craniotomy is the surgical removal of part of the bone from the skull to expose the brain. Specialized tools are used to remove the section of bone called the bone flap. The purpose of the procedure is to remove a brain tumor or a sample of brain tissue. It may also be done to remove blood or blood clots from the brain, relieve pressure in the brain after an injury or stroke, repair a skull fracture or brain aneurysm (a bulge in a blood vessel wall), or treat other brain conditions. The bone flap is replaced after the brain surgery has been done.

Endoscopic surgery is minimally-invasive, meaning it does usually not require a large incision. Neurosurgeons may make a small opening inside the nose to remove a growth through a thin lighted tube called an endoscope. An MRI is a type of picture taken of the skull base using magnets and a computer and may be done by a radiology specialist while the surgical specialists are operating to help them make sure all of the growth has been removed.

This is the most common way to remove pituitary tumors. Transsphenoidal surgery is done through the sphenoid sinus, a hollow space in the skull behind the nasal passages and below the brain. The back wall of the sinus is just below the pituitary gland.

This minimally invasive surgical tool removes hematomas with low tissue disruption, protecting parts of your brain that control speech, memory and vision. The neurosurgeon is able to navigate between the natural folds in the brain and map the exact location of the tumor or blood clot using imaging. Then, through an opening no larger than a dime, the neurosurgeon can remove the clot or tumor from the deepest recesses of the brain without cutting or damaging anything else in its path.

CyberKnife uses stereotactic body radiation therapy, delivering precise doses of radiation with extreme accuracy—accounting for tumor or patient movement in real-time. The robot moves and bends around the patient to deliver radiation doses from thousands of unique beam angles, significantly expanding the possible positions to concentrate radiation to the tumor while minimizing dose to surrounding healthy tissue.

Neurosurgeons work closely with interventional radiologists, neurologists, oncologists and staff. Specialists contribute expertise in brain anatomy, skull base pathology, imaging, neurological function and oncological considerations. A collaborative effort ensures comprehensive patient evaluation, precise surgical planning, and optimal postoperative care, leading to improved outcomes.

Our team of top-rated neurosurgeons and other specialists work collaboratively to diagnose and treat patients from infants to adults. With state-of-the-art technology and leading research, our expert surgeons treat brain tumors, spinal disorders, neurosurgical cancers, movement disorders, endovascular issues and other complex neurological conditions.

Our skilled team of neurosurgeons, neurologists and other specialists work collaboratively to diagnose and treat patients of all ages.

State-of-the-art expertise in treating brain tumors, spinal disorders, cancers, vascular issues and other complex neurological conditions.

1st in VA to offer deep brain stimulation for epilepsy; and 1st in VA to implant a Vagal Nerve Stimulator for depression treatment.

Regional leader in neurosurgical research and clinical trials.



Our skilled team of neurosurgeons, neurologists and other specialists work collaboratively to diagnose and treat patients of all ages.

State-of-the-art expertise in treating brain tumors, spinal disorders, cancers, vascular issues and other complex neurological conditions.

1st in VA to offer deep brain stimulation for epilepsy; and 1st in VA to implant a Vagal Nerve Stimulator for depression treatment.

Regional leader in neurosurgical research and clinical trials.


Learn about your diagnosis and symptoms
Carilion Clinic believes that education empowers patients to take an active role in their health. Patients and families can learn more about medical conditions and healthy living to better care for themselves.
Experts leading the way with

It was the only path I had for a normal lifestyle. Dr. Marvin goes over and above to [make that happen]."
Kay Moyer
, Neurosurgery
Our Skull Base Neurosurgery team includes specialists in neurosurgery, head and neck surgery, sinus and skull base surgery, ENT, neuroradiology and radiation oncology. A nurse practitioner and other care team members ensure seamless care for our patients.
Contact UsOffering state-of-the-art expertise in treating brain tumors, spinal disorders, cancers, vascular issues and other neurological conditions.
Contact us for a consultation in a location near you!
To schedule an appointment at a Skull Base Neurosurgery location
View All Locations
Access to Care
Call 540-224-5170